Excel Conditional Formatting — 9 Best Uses (Bonus Video)
This Conditional Formatting in Excel tutorial is suitable for users of Excel 2010, 2013,2016,2019, and Microsoft 365.
Objective
Use Excel Conditional Formatting to highlight important data visually and identify patterns and trends.
Excel Conditional Formatting Explained
Have you ever come across beautiful-looking Excel sheets that are visually appealing to the viewer, highlighting important data points without creating any clutter?
That is the power of Excel conditional formatting.
It takes your data and presents it to the audience in a very intuitive, easy-to-understand way.
If used properly, it can even make your presentation, everyone’s centre of attention.
Related:
Excel Sumifs & Sumif Functions – The No.1 Complete Guide
Create An Excel Dashboard In 5 Minutes – The Best Guide
Dynamic Dropdown Lists In Excel – Top Data Validation Guide
Conditional formatting in Excel changes the appearance of a cell or a range of cells based on the conditions you specify. It makes it easy to highlight important information in a dataset, detect issues, emphasize anomalies, and visually analyze data using data bars, colour scales, and icon sets.
There are many built-in Excel conditional formatting styles for use, or you can create custom formats.
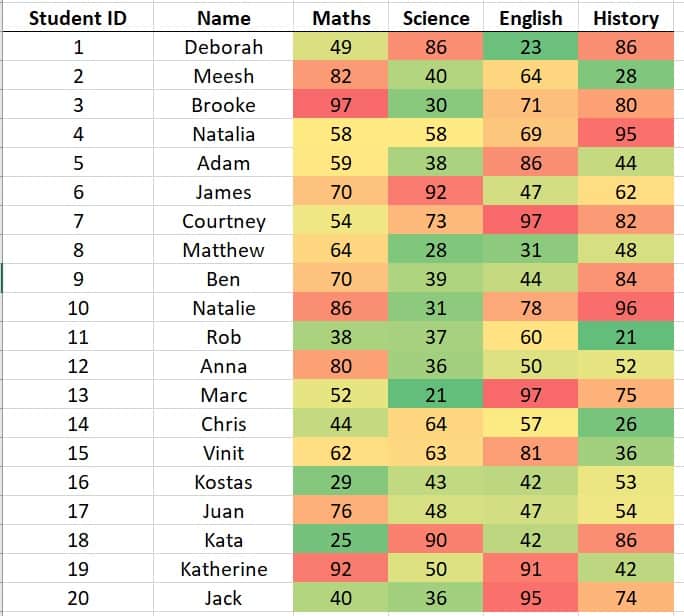

Higher test scores are more orange/red, while lower test scores are more yellow/green
Conditional Formatting can be applied to numerical datasets (either a selection or named range), and an Excel table or even a PivotTable report.
Video Tutorial – Conditional Formatting in Excel
To see Excel Conditional Formatting in action, please watch the following video tutorial.
Excel Conditional Formatting – 9 Common Uses
There are many different types of Conditional Formatting in Excel. Let us explore some of the most useful.
- Format cells that are greater than or less than a number
- Format cells that contain text
- Format only top or bottom ranked values
- Format cells using data bars
- Format cells using colour scales
- Format cells using an icon set
- Use a formula to determine which cells to format
- Highlighting an entire row based on the value of a cell
- Managing and clearing Excel conditional formatting
Now let’s jump right into each of these uses and see how things are done in detail.
But as a precursor,
- Select the range of cells you want to apply Conditional Formatting to
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
1.Format cells that are greater than or less than a number
In this example, I want to format all the cells that contain a test score greater than 75.
- Select the cell range that contains the test scores
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Highlight Cells Rules
- Click Greater Than
- Enter the number 75
- Select a formatting option
- Click OK
Excel will format all the cells that contain a test score of 75 or above.
You can use the same method to find test scores lower than a specified number by selecting the Less Than menu option from the Highlight Cells Rules drop-down.
2.Format cells that contain text
Cells can be formatted based on the text contained within them. For example, in this range, I want to format all of the cells in column C that contain the word ‘Beatles.’
- Select column C
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Highlight Cells Rules
- Click Text that Contains
- Enter the text ‘Beatles’
- Select a formatting option
- Click OK
You can use the same method to find specific dates in a range and duplicate values.
Also Read:
Predict Future Values Using Excel Forecast Sheet – The Best Guide
Getting Started With Excel 3d Maps – The Top 5 Steps
Excel Dynamic Array: 8 Must-know Formulas
3.Format only top or bottom ranked values
You can find the highest and lowest values in a range of cells based on the criteria you specify. In this example, I want to find which students rank in the top 10% for history.
- Select the History column
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Top/Bottom Rules
- Click Top 10%
- Use the scroll arrows to adjust the percentage if required
To format cells using different colours other than the ones specified in the list, click Custom Format.
- Click OK
You can use the same method to format the bottom 10%, the top/bottom items, and those above or below average.
4.Format cells using data bars
Data bars help you visualize values in cells relative to other values. The length of the data bar represents that value in the cell. The longer the bar, the higher the value.
- Select a range of cells
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Data Bars
In this example, I have applied Gradient Fill to the Maths and Science columns and Solid Fill to the English and History columns.
5.Format cells using colour scales
Colour scales are visual guides that help you understand how data is distributed. Like a heat map, colour scales are useful in helping you visualize variations in data. You can apply two-colour scales or three-colour scales to a data range, and the value in each cell is represented by two or three colours depending on which colour scale you selected.
- Select a range of cells
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Color Scales
In this example, I have used a two-colour scale. The higher values have a yellow colour and the lower values are green.
6.Format cells using an icon set
Icon sets are used to group or classify data into three to five categories. They make it easy to visualize values in a range of cells with each icon representing a range of values. For example, if you select a 3-icon set to apply to a range of cells, Excel looks at the values in the selected cells and calculates the 67th and 33rd percentile. It then assigns an appropriate icon depending on which 3rd the value falls in.
- Select a range of cells
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Icon Sets
In this example, I have selected the ‘3 Traffic Lights’ icon set. Excel has assigned the red traffic light to the values that fall in the lowest third, the orange traffic light to the values that fall in the middle third, and the green traffic light for values that fall in the highest third.
7.Use a formula to determine which cells to format
Formulas can be utilized with Excel conditional formatting. You can use a logical formula to specify the formatting criteria and create your own conditional formatting rule.
- Select a range of cells
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click New Rule
- Select Use a formula to determine which cells to format
- Type the formula into the Format values where this formula is true field
- Click Format
- Select the desired formatting style
- Click OK
In this example, I have created a rule that contains a formula to find all the cells in the selected range that contain an odd value and format those cells with a purple background fill and white font. The cell reference in brackets (C7) is the only argument for the ISODD function. The cell reference used should always be the top left-most cell in the selected dataset.
All odd numbers in the dataset are now formatted.
8.Highlighting an entire row based on the value of a cell
You can create an Excel conditional formatting rule that highlights an entire row based on the value of a cell. It is much easier to visualize important data when the whole row is highlighted rather than a specific cell, particularly if you have a large dataset.
- Select a range of cells
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click New Rule
- Select Use a formula to determine which cells to format
- Type the formula into the Format values where this formula is a true field
- Click Format
- Select the desired formatting style
- Click OK
In this example, I have created a rule that highlights all rows that contain the name ‘Deborah Ashby.’ The cell reference $E4 is used as it is the first cell in the column that contains the text string I am searching for. When you copy this formula down, the row number (4) is not locked but the column letter (E) is.
9.Managing and clearing Excel conditional formatting
Conditional Formatting rules can be edited, deleted, and cleared.
Edit and delete using the Rules Manager
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Manage Rules
- Select a rule from the list
- Click Edit Rule to make changes
- Click Delete Rule to remove from the list
- Click OK
Clear Formatting Rules
Conditional Formatting can be cleared from the selected cells or the entire sheet.
- Click the Home tab
- Click Conditional Formatting
- Click Clear Rules
Suggested Reads:
Excel For Beginners – Formula Bootcamp
Macros And Basic Vba In Excel – Recorded Webinar
Importing And Cleaning Data In Excel
To see more ways of using Excel conditional formatting to highlight data in your worksheet, check out the following links:
Microsoft – Use Conditional Formatting to highlight important information
Spreadsheeto – How to Use Conditional Formatting in Excel: 15 Awesome Tricks
FAQs
How do you do conditional formatting in Excel based on another cell value?
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format. Go to Conditional Formatting and select Format by Formula. Enter the formula which refers to the other cell, based on which you want to format. Click Format to Proceed with Formatting Style.
Can I copy conditional formatting from one cell to another cell?
Select the cells that you want to copy. Locate and click the format painter button in the Home Ribbon. Now, drag the brush icon across the cells that you want the conditional formatting to be copied to.
For more Free Excel tutorials from Simon Sez IT. Take a look at our Excel Resource Center.
To learn Excel with Simon Sez IT. Take a look at the Excel courses we have available.

